They are currently used for the diagnosis of food allergies are the most common screening test for food allergies and can also be performed on infants in the first months of life (Sopo reliable, however after 3 years). However, the reliability of the results depends on many factors, such as the use of allergens should be tested together with a precise technique of administration, and concomitant medications that may interfere with tests such as for example: antihistamines or cortisone.
When these tests are used with appropriate controls as standard, for example, a test with a positive sample on the basis of histamine and a negative-based saline; provide precise criteria for the diagnosis easily reproducible with minimal cost and with negligible risks for patients . This method is generally reliable for excluding immediate food allergies, with a predictive accuracy of 90% if the result is negative, while this accuracy drops to 50% if positive. This limits the interpretation of clinical results, and then together with in vitro tests should also consider the history.
The result is always confirmed by a test read ministration incorminato food, unless the patient already has a history of allergy to some food.
Method
The intradermal tests are:
∙ prick test
∙ prick by prick (English: to prick prick =)
∙ scracth tests
∙ patch testing.
These are used both for food allergies and for respiratory allergies.
For the interpretation of the tests required experience and expertise, and the results obtained, in fact, should always be related to symptoms and history of patients and often require additional testing to establish a diagnosis of certainty.
During the execution of these tests you need to keep on hand an emergency kit, it can, albeit rarely, severe reactions occur, up to anaphylactic shock.
The skin prick test, if repeated several times with the same allergen, in turn, can cause sensitization.
The prick by prick is used only for food allergies in this method the needle used to scratch the skin of the patient is pre-inoculated in the food you want to test (fruit or vegetables).
Scracth The test is similar to the skin prick test but is less sensitive and more long-running, so now little used. After cleaning the skin with a sharp instrument practice is a slight scratch (in English, scratch) of 2 mm in length without bleeding, after which a drop of solution containing the allergen is placed above the lesion caused and gently you make a scratched rubbing the area to make it the solution to penetrate into the lesion, the reading is done after 10-30 min.
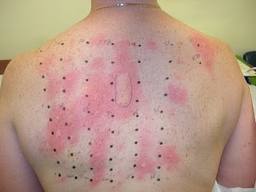
The patch test is indicated in the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis. It consists in the skin of the back of medicated patches with the allergen, they are routinely tested 31 allergens. The patch is removed after 24-72 hours, and check whether the application area of skin redness occurred. This test is used in food allergies to ensure responsiveness to food in case of eosinophilic esophagitis, enterocolitis and atopic dermatitis. The value of this test, however, is uncertain and should be confirmed by more objective than those of studies conducted to date.
∙ Are made on the appropriate region of the forearm with thin-tipped hands that inject the allergen to be tested, it is important to use a lancet for each allergen, respecting the minimum distance between an allergen and another (2.5 cm).
∙ Comparisons are made with the negative controls with saline and positive control with histamine (10 ng / mL in G. Physiological).
∙ The reading should be done after 5 min for histamine and after 15 for allergens, it is advisable to use a stopwatch. They are of dubious responses that occur after 15-20 min.
∙ The tests are not very risky, but it is good to do a preliminary test with the allergen is not inoculated subcutaneously with the needle and see if looks like a reaction, in which case you should not test for the risk of a severe reaction type anaphylactic (as well as the uselessness of the test in this circumstance).
Limitations of skin testing
In general, these tests are used on individuals aged less than 3 years. However, should not be made in the following cases:
1. lesions from scratching or skin diseases in the area of administration of the test.
2. dermographic patients, for a heightened responsiveness on the part of the skin from these patients.
3. use of antihistamines and / or steroids and / or immunosuppressive agents, which inhibit the immunological mechanisms and thus the reactivity of the skin (may have the same effect, although a much lesser extent, beta-blockers).